Situational Leadership - Meaning and Concept
Situational Leadership - Meaning and Concept
Leaders are essentially people who know their goals and have the power to influence the thoughts and actions of others to garner their support and cooperation to achieve these goals. In-case of leaders these goals are rarely personal and generally to serve the larger good.
Ever since man was a hunter gatherer and lived in closely knit groups, they had leaders who led the hunting expeditions and took greater risk than the rest of the group members. In turn they were bestowed with larger share of hunting, respect and a higher position in the group. With changing times, how leadership is perceived has also changed, but, it remains an important aspect of social fabric nevertheless.
The initial theories proposed that leaders are born and cannot be created, there are certain distinct characteristics possessed by few men which make them leaders. [Read Great Man Theory and the Trait Theory]. However, for the current discussion we would try and take a closer look at another interesting theory which was proposed called Situational Leadership Theory. This theory says that the same leadership style cannot be practiced in all situations, depending upon the circumstance and environmental context the leadership style also changes. The pioneers of this theory were Kenneth Blanchard and Paul Hersey.
The model encourages the leaders to analyze a particular situation in depth and then lead in the most appropriate manner, suitable for that situation. The three aspects that need could be considered in a situation are:
- Employees’ competences
- Maturity of the employees
- Complexity of the task
- Leadership style
In the Situational Leadership model, the leadership style has been divided into 4 types:
- S1: Telling - Telling style is associated with leaders who minutely supervise their followers, constantly instructing them about why, how and when of the tasks that need to be performed.
- S2: Selling - Selling style is when a leader provide controlled direction and is a little more open and allows two way communication between him/herself and the followers thus ensuring that the followers buy in the process and work towards the desired goals.
- S3: Participating - This style is characterized when the leaders seeks opinion and participation of the followers to establish how a task should be performed. The leader in this case tries creating relationship with the followers.
- S4: Delegating - In this case, the leader plays a role in decisions that are taken but passes on or delegates the responsibilities of carrying out tasks to his followers. The leader however monitors and reviews the process.
It is also represented by a diagram most often which is below:
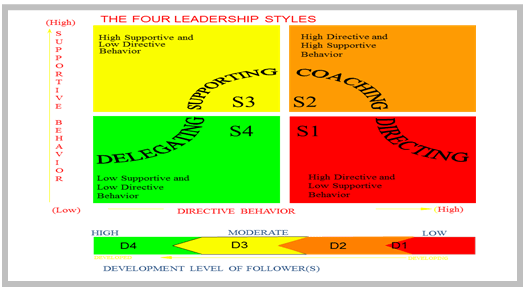
The developmental level of follower is an important indication for a leader to decide the most appropriate leadership style for them:
- D4 - High Competence, High Commitment - The followers who are identified in this category are the ones who have high competence and high commitment towards tasks to be performed. It might happen so that they turn out better than their leaders in performing these tasks. (For e.g. cricketing legend Sachin Tendulkar playing in the Indian cricket team under the captainship of Mahendra Singh Dhoni)
- D3 - High Competence, Variable Commitment - This category consists of followers who have the competence to do the job but their commitment level is inconsistent. They also tend to lack the confidence to go out and perform task alone. (E.g. President Barack Obama)
- D2 - Some Competence, Low Commitment - In this case, the followers have a certain level of competence which might be sufficient to do the job but they are low on commitment towards the tasks. Despite of having relevant skills to perform the task they seek external help when faced with new situations. (A team member made the trainer for new joiners)
- D1 - Low Competence, High Commitment - This category of followers may not have the specific skill required but they display a high level of commitment towards the task they have to perform, with confidence and motivation, they figure out ways to complete the tasks. (E.g. Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, a lawyer by profession who spearheaded the Indian Freedom Struggle)
The above information regarding the style of leadership and the type of followers sure has a correlation to each other which forms the basis of situational leadership. So, a situational leader would try to accommodate his leadership style as per the situation and the level of competence and commitment of his followers. This information is also an important aspect to consider when senior leaders act as coaches for their subordinates in the organizations.



/top-leadership-skills-2063782_final-5b3e6be646e0fb0036272f42-5bbf7e0246e0fb0026d6416a.png)
)




