Database Design - Overview, Importance, and Techniques | Astera
All You Need to Know About Database Design
By Tehreem Naeem|October 1st, 2019
A database includes bulk information deposited in a framework, making it easier to locate and explore relevant information. A well-designed database contains accurate and up-to-date information, allowing data to be fetched easily whenever needed. It is easy to understand the importance of a database for a company dealing with heaps of data regularly. However, it is significant to note that it requires a data design that can make analysis faster and reliable.
In this blog, we’ll answer a common question—what is the database design process? Moving ahead we’ll discuss the importance of database design and how it can benefit your data endeavors. We’ll also go through some of the most common database design techniques to give you an insight into how to design a database. Lastly, we’ll cover basic steps and best practices to help you design a good database for your organization.
What is Database Design?
Database design is defined as a collection of steps that help with designing, creating, implementing, and maintaining a business’s data management systems. The main purpose of designing a database is to produce physical and logical models of designs for the proposed database system.
What is a Good Database Design?
A good database design process is governed by specific rules. The first rule dictates that redundant data must be avoided; as it wastes space and increases the probability of faults and discrepancies within the database. The next rule is that the accuracy and comprehensiveness of information is extremely imperative. If the database contains erroneous information, any documents that fetch data from such a database will also include inaccurate information. Consequently, any decisions based on those documents will be misleading, thus, increasing the importance of a database design that caters to all of the above rules.
So, how can you ensure that your database design is good? A well-designed database is the one that:
- Distributes your data into tables based on specific subject areas to decrease data redundancy
- Delivers the database the information needed to link the data in the tables
- Provides support, and guarantees the precision and reliability of data
- Caters to your information processing and reporting requirements
- Functions interactively with the database operators as much as possible
ETL Your Enterprise Data Using MYSQL Connector
Move MySQL Data to a Destination of Your Choice Through a Codeless, Drag-and-Drop UI.
Importance of Database Design
Database design defines the database structure used for planning, storing, and managing information. Accuracy in data can only be accomplished if a database is designed to store only valuable and necessary information.
A well-designed database is significant in guaranteeing information consistency, eliminating redundant data, efficiently executing queries, and improving the performance of the database. Meticulously designing a database saves you from wasting time and getting frustrated during the database development phase. A good database design also allows you to easily access and retrieve data whenever needed.
The reliability of data depends on the table structure; whereas creating primary and unique keys guarantees uniformity in the stored information. Data replication can be avoided by forming a table of probable values and using a key to denote the value. So, whenever the value changes, the alteration happens only once in the main table.
As the general performance of a database depends on its design, a good database design uses simple queries and faster implementation. It is easy to maintain and update; whereas fixing trivial interruptions in a poor database design may harm stored events, views, and utilities.
Database Development Life Cycle
There are various stages in database development. However, it is not necessary to follow each of the steps sequentially. The life cycle can be broadly divided into three steps: requirement analysis, database designing, and implementation.
1- Requirement Analysis
Requirement analysis requires two steps:
- Planning: In this stage, the plan of the entire Database Development Life Cycle is decided. It also requires an analysis of the organization’s information systems strategy.
- Defining the system: This stage explains and lays out the proposed database system’s scope.
2- Database designing
The actual database designing takes into account two key models:
- Logical model: It is concerned with using the given requirements to create a database model. The complete design is laid out on paper at this stage, without considering any specific DBMS requirement or physically implementing it.
- Physical model: This stage comes after the logical model and therefore involves physically implementing the logical model. It takes the DBMS and other physical implementation factors into consideration.
3- Implementation
The implementation stage of the database development life cycle is concerned with:
- Data conversion and loading: It comprises data importation and data conversion coming from the old system into the new database.
- Testing: Finally, this stage identifies errors in the new system and make sure if all the database requirement specification are met.
Database Designing Techniques
The two most common techniques used to design a database include:
- Normalization: Tables are organized in such a way that it decreases data redundancy and dependency. Larger tables are divided into smaller tables and are linked together using relationships.
- Entity-Relationship (ER) Modeling: It’s a graphical database design approach that models entities, their attributes, and defines relationships among these entities to signify real-life objects. An entity is any real-world item that’s different or unique from the surroundings.
Implement Virtual Database
Implement Virtual Database Tools to Provide Business-Users the Accessibility and Flexibility They Require to Analyze Data.
How to Design Database: Steps of Designing Database
The first question you need to ask when designing a database is, how will you specify the structure of the database?
Database designing generally starts with identifying the purpose of your database. The relevant data is then collected and organized into tables. Next, you specify the primary keys and analyze relationships between different tables for an efficient data design. After refining the tables, the last step is to apply normalization rules for table standardization.
Let’s look at these steps of database design in detail:
- Define the objective of your database
The first step is to determine the purpose of your database. For example, if you are a small home-based business, you could be designing a customer database that maintains a list of consumer info to generate emails and reports. Hence, understanding the importance of a database is vital.
At the end of this step, you’ll have a strong mission statement that you can refer to throughout the database design process. It’ll help you concentrate on your objectives when making important decisions.
- Locate and consolidate the necessary data
The next step is to collect all kinds of information that you might want to store in the database. Begin with the current information. Mull over the questions you want your database to answer, and it’ll help you decide which data needs to be recorded.
- Distribute the data into tables
Once you’ve amassed all the necessary data items, the next step is to divide them into main entities or subject areas. For example, if you are a retailer, some of your main entities could be products, customers, suppliers, and orders. Each entity will then become a separate table.
- Change data items into columns
Data is segregated into tables, such that every data item becomes a field and is shown as a column. For instance, a Customer table might include fields like name, address, e-mail address, and city.
After determining the preliminary set of columns for every table, you can refine them. For instance, customer name can be recorded as two distinct columns: first name and last name. Likewise, you can store the address in five distinct columns based on address, town, state, zip code, and region. This will make it convenient for you to filter information.
Streamline Cross-Database Analysis
Access the MariaDB Database and Create a Holistic View of Your Data Through Codeless Integration.
- Identify primary keys
The next step to improve your database design is to select a primary key for every table. This primary key is a column or a set of column that’s used to distinctively pinpoint each row. For instance, in your customer table, the primary key could be customer ID. This will allow you to uniquely identify each row based on the customer ID.
More than one primary key can also exist, called a composite key, including multiple columns. For example, in your Order Details table, primary keys could be order ID and product ID. The composite key can be made using fields with similar or varying data types.
Similarly, if you wish to get an idea of your product sales, you can identify the product ID from the Products table and the order number or ID from the Orders table.
- Determine how tables are related
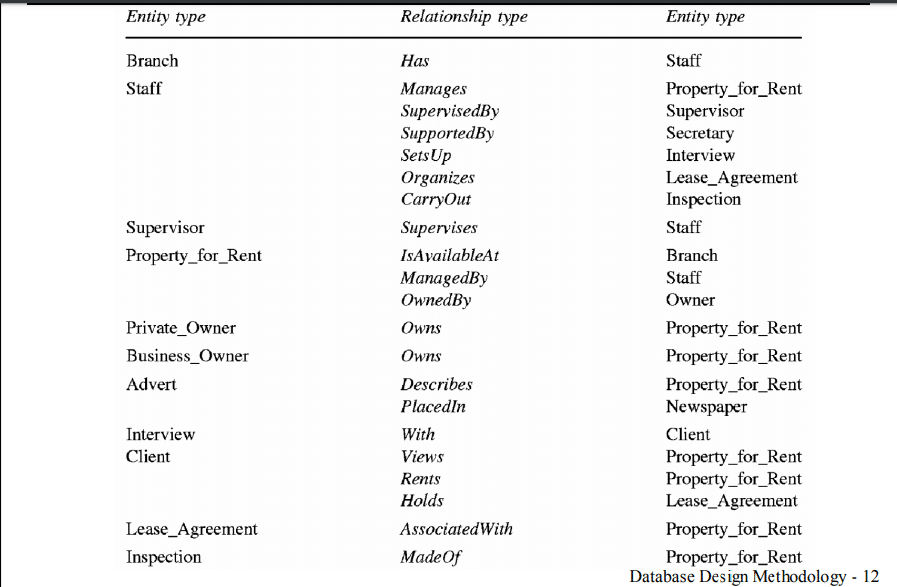
After dividing data into tables, information needs to be brought together in a meaningful manner. So, explore each table and determine how the data in one table is linked with the data in another table. If needed, you can add fields or form new tables to simplify the relationship based on the types of information.
Below is an example of different entity types and relationship types.
Source: City University of Hong Kong
In this step, you’ll create one-to-one, one-to-many, and/or many-to-many relationships between different table entries.
When only one item from a table is associated with an item from another table, it’s called a one-to-one (1:1) relationship. In a one-to-many (1:M) relationship, an item in one table is related to many items in the other table, such as one customer placing several orders. A many-to-many (M:N) relationship occurs if many items from one table are related to many items in other tables.
Source: GerardNico
- Enhance your database design
Now that you have all the required tables, fields, and relationships, the next step is to refine your database design by creating and populating your tables with mockup information. Experiment with the sample data by creating queries or adding new items. This will help you analyze your design for faults and you’ll be able to highlight possible errors. If needed, adjust your design to mitigate those problems.
- Implement the normalization rules
The last step is to implement the normalization rules for your database design. It is a systematic approach that removes redundancy and unwanted characteristics, such as Insertion, Update, and Deletion irregularities.
This multi-step process stores data in a tabular form, eliminating redundant data from the relation tables.
Final Words
Let’s summarize what a database design is. The database design process helps you simplify the design, development, execution, and maintenance of your corporate data management system.
A good database design can help save disk storage space by reducing data redundancy. Along with maintaining data precision and reliability, it allows you to access data in various ways. Moreover, a well-designed database is easier to use and maintain, making integration a breeze.